Intoroduction
In this tutorial we will see how to use ElementCollection to implement one to many mapping in spring boot application. In our previous example we have used one-to-many mapping, but here we are using ElementCollection fron JPA which is a very simple than regular one-to-many mapping soluion. We are going to learn how to use these two annotations
@ElementCollection and
@CollectionTable.
Database Schema
Consider a simple example where Product has multiple manufacturers and suppliers. Here we are going to create three database tables named as product, manufacturer and supplier
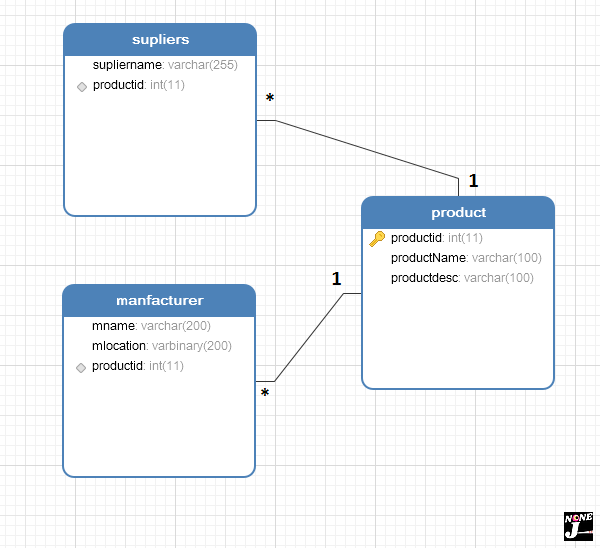 |
| Database schema for product |
Dependencies to add in pom file
we need to add web, jpa and mysql driver dependencies into pom file
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
Database related properties
Then we need to set configurations in application.properties file for hibernate and mysql connection
# Database connection details
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jai43?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC&useLegacyDatetimeCode=false
spring.datasource.username=jai43user
spring.datasource.password=123456
# hibernate as JPA imlementation
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
# this to let the spring boot to perfrom database schema update whene there is a changes in entity class
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
Creating Embeddable model Classes
This is the major step here we can see the differences than regular one-to-mapping and
ElementCollection. We are going to create Manufacturer and Supplier model classes as
embeddable class type.
Creating embeddable model class
By using @Embeddable a class level annotation can be used to create embeddable model class
@Embeddable
public class Manufacturer {
@NotNull
String manufacturerName;
@NotNull
String mlocation;
public Manufacturer(@NotNull String manufacturerName, @NotNull String mlocation) {
super();
this.manufacturerName = manufacturerName;
this.mlocation = mlocation;
}
public String getManufacturerName() {
return manufacturerName;
}
public void setManufacturerName(String manufacturerName) {
this.manufacturerName = manufacturerName;
}
public String getMlocation() {
return mlocation;
}
public void setMlocation(String mlocation) {
this.mlocation = mlocation;
}
}
For supplier database table we are not going to create a separate model class, because it has only one field other than foreign key, so in a person entity class directly we can map with String type.
Creating Entity class for parent table ( product table )
Here product table is a parent table for manufacturer and supplier table. We are going to use @ElementCollection and @CollectionTable annotations to establish one to many mapping.
@Entity
@Table(name = "product")
public class Products {
@Column(name = "productid")
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
Long pid;
@Column(name = "productname")
@NotNull
@Size(max = 100)
String pname;
@Column(name = "productdesc")
@NotNull
@Size(max = 100)
String pdesc;
// here we are going to use ElementCollection to enable Supplier table
@ElementCollection
@CollectionTable(name = "supliers", joinColumns = @JoinColumn(name="productid"))
@Column(name = "supliername")
Set<String> suppName= new HashSet<String>();
// ElementCollection for Manufacturer table with embeddable model class
@ElementCollection
@CollectionTable(name = "manfacturer",joinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "productid"))
@AttributeOverrides({
@AttributeOverride(name = "manufacturerName", column = @Column(name="mname"))
})
Set<Manufacturer> man = new HashSet<Manufacturer>();
public Products( @NotNull @Size(max = 100) String pname, @NotNull @Size(max = 100) String pdesc) {
super();
this.pname = pname;
this.pdesc = pdesc;
}
public Products( @NotNull @Size(max = 100) String pname, @NotNull @Size(max = 100) String pdesc,
Set<String> suppName, Set<Manufacturer> man) {
super();
this.pname = pname;
this.pdesc = pdesc;
this.suppName = suppName;
this.man = man;
}
}
Repository for products
@Repository
public interface ProductRepository extends JpaRepository<Products, Long> {
}
Inserting operation
String pname="Phone";
String pdesc="Mobile phone for calling";
Set<String> suppls= new HashSet<String>();
suppls.add("Samsung");
suppls.add("Apple");
Set<Manufacturer> man= new HashSet<Manufacturer>();
man.add(new Manufacturer("Samsung", "India"));
// Without inserting values into supplier and manufacturer table
Products p= new Products(pname, pdesc);//, suppls, man);
pr.save(p);
// With insertion of supplier and manufacturer
Products p= new Products(pname, pdesc, suppls, man);
pr.save(p);
output
 |
| output of one to many mapping with ElementCollection |
Further Reading





 Posted by: jaya
Posted by: jaya

Post a Comment
Post a Comment