Introduction
Java8 has come up with great features than previous java versions, Stream is a part of util package, map() and flatMap() are two important intermediate methods of Stream to perform Stream transformation and flattening operations.
Stream<t> will be input for map() and then Stream<R> will be output of map() after applying functional logic on each element of Stream<T>. For example Stream<String> which holds Employee names of organisation, after applying map() output will be Stream<Integer> which stores length of employee names, so here the functional logic is getting length of employee name.
map() method is only doing transfermation of one Stream into another type of Stream
map() method
Method map() will take every element of Stream as an input and returns one output to each and every input, thats why it is called as one-to-one mapping function.
map() with non nested list/Stream
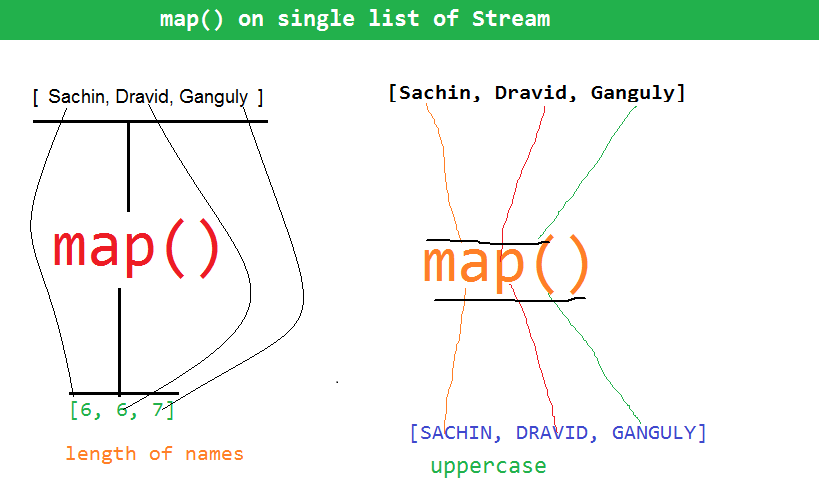 |
| Stream transformation of list with map() |
Each input has output when we use map() to transform into new Stream
In the above figure Stream of names converted/transformed into Stream of lengths( Integers) and in scond example converted into Steam of uppercase names. List<String> names = new ArrayList<String>();
names.add("Sachin");
names.add("Dravid");
names.add("Ganguly");
Stream<String> namesStream = names.stream();
Stream<Integer> namesLengthStream = namesStream.map(name -> name.length());
List<Integer> namesLengthList = namesLengthStream.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("names list:- " + names);
System.out.println("Names length list:- " + names.stream().map(na -> na.length()).collect(Collectors.toList()));
System.out.println("Names inti uppercase as list:- " + names.stream().map(na -> na.toUpperCase()).collect(Collectors.toList()));
output:names list:- [Sachin, Dravid, Ganguly]
Names length list:- [6, 6, 7]
Names inti uppercase as list:- [SACHIN, DRAVID, GANGULY]
map() with nested list/Stream
Here we can apply map() on nested list/stream, but here we have to use nested map() to perform operations on nested list
 |
| nested map() with nested list/stream |
List<String> names = new ArrayList<String>();
names.add("Sachin");
names.add("Dravid");
names.add("Ganguly");
List<String> namesTwo = new ArrayList<String>();
namesTwo.add("SachinTwo");
namesTwo.add("DravidTwo");
namesTwo.add("GangulyTwo");
List<String> names3 = new ArrayList<String>();
names3.add("SachinThree");
names3.add("DravidThree");
names3.add("GangulyThree");
List<List<String>> namesList = new ArrayList<>();
namesList.add(names);
namesList.add(namesTwo);
namesList.add(names3);
System.out.println("Names Nested list:- " + namesList);
System.out.println("Names into uppercase:- "
+ namesList.stream().map(namesa -> namesa.stream().map(
el -> el.toUpperCase()).collect(Collectors.toList()))
.collect(Collectors.toList()));
System.out.println("Names length list:- "
+ namesList.stream().map(namesa -> namesa.stream().map(
el -> el.length()).collect(Collectors.toList()))
.collect(Collectors.toList()));Names Nested list:- [[Sachin, Dravid, Ganguly], [SachinTwo, DravidTwo, GangulyTwo], [SachinThree, DravidThree, GangulyThree]] Names into uppercase:- [[SACHIN, DRAVID, GANGULY], [SACHINTWO, DRAVIDTWO, GANGULYTWO], [SACHINTHREE, DRAVIDTHREE, GANGULYTHREE]] Names length list:- [[6, 6, 7], [9, 9, 10], [11, 11, 12]]In the output you can notice that map() produce indivedual output for each indivedual input element. If we want to combine all nested streams into a single stream we need to perform flattening operation which is possible with flatMap() method. For example if we want to get output as single stream [SACHIN, DRAVID, GANGULY, SACHINTWO, DRAVIDTWO, GANGULYTWO, SACHINTHREE, DRAVIDTHREE, GANGULYTHREE] is not possible with map(), here we need to use flatMap()
flatMap()
Method flatMap() if Stream is useful to apply mapping and flattening on a Stream/Collection of Streams/Collections format( Collection<Collection<T>> -> flatMap() -> Collection<T>).
 |
| flatMap() on Stream of Streams |
System.out.println("Names flattening with flatMap:- "+
namesList.stream().flatMap(
x -> x.stream()
).collect(Collectors.toList()));
System.out.println("Names into uppercase with flatMap:- " +
namesList.stream()
.flatMap(namesl -> namesl.stream()).map(
nl -> nl.toUpperCase()
).collect(Collectors.toList()));
Names flattening with flatMap:- [Sachin, Dravid, Ganguly, SachinTwo, DravidTwo, GangulyTwo, SachinThree, DravidThree, GangulyThree] Names into uppercase with flatMap:- [SACHIN, DRAVID, GANGULY, SACHINTWO, DRAVIDTWO, GANGULYTWO, SACHINTHREE, DRAVIDTHREE, GANGULYTHREE]



 Posted by: jaya
Posted by: jaya

Post a Comment
Post a Comment